Inhibition of ERAP1 or ERAP2 upregulates and creates novel cancer antigens, resulting in improved immunogenicity, the generation of anti-cancer CD8+ T cell responses and tumour growth inhibition. Grey Wolf is developing novel, first-in-class ERAP inhibitors that upregulate immunogenic neoantigens at the tumour cell surface and these can be recognised by the immune system.
Hover over each of the interactive dots to learn more about the antigen presentation pathway
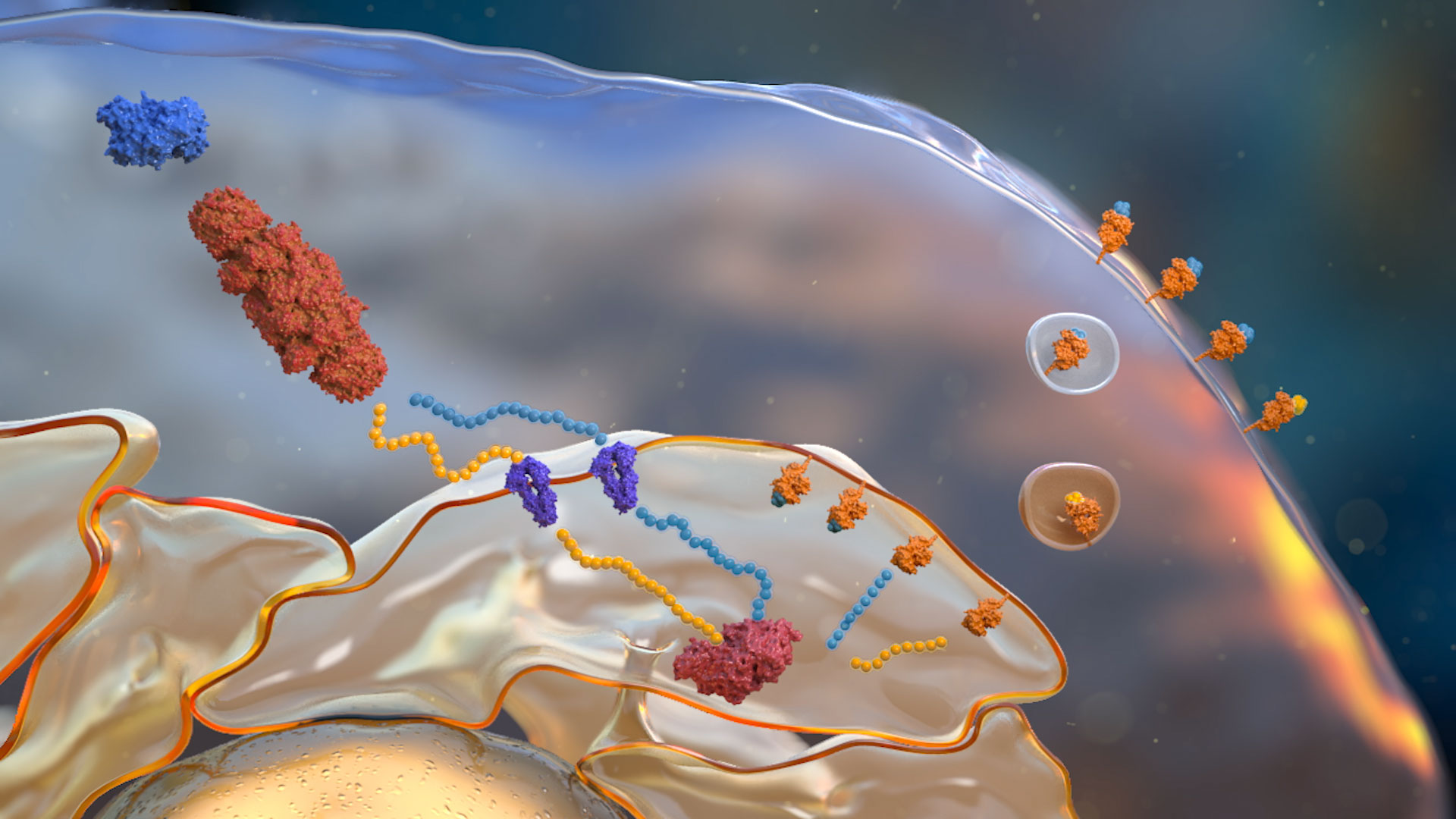
Multiple sources of protein that feed the antigen presentation pathway.
The majority of peptides that feed the antigen presentation pathway are degraded by the proteasome.
Peptides generated by the proteasome are transported into the ER.
Peptides from the cytosol are transported into the ER via the TAP transporter complex.
ER resident aminopeptidases which trim or over-trim antigens and neoantigens prior to loading onto MHC Class I. ERAP1 and ERAP2 have different peptide specificities.
At the cell surface the MHC Class I complex presents antigens / neoantigens to CD8 T cells where they are recognised as ‘self’ or 'non-self’.
Peptides loaded onto the MHC Class I complex through the action of the Peptide Loading Complex (PLC) and ERAP1/2 activity are transported to the cell surface.